

After a stroke or a traumatic brain injury, patients often lose control of their arms and hands. This makes carrying out any basic task difficult without assistance.
This is why physical therapy plays an important role in rehabilitation. Physical therapists suggest the most appropriate ways to support neuroplasticity and get the brain rebuilding signals to muscles in your arms. This includes exercises to simulate basic movements. So, what arm exercises can you perform to improve rehabilitation?

Basic stretches are important to regain full arm strength. Stretching reduces the risk of spasticity as well as joints stiffening.
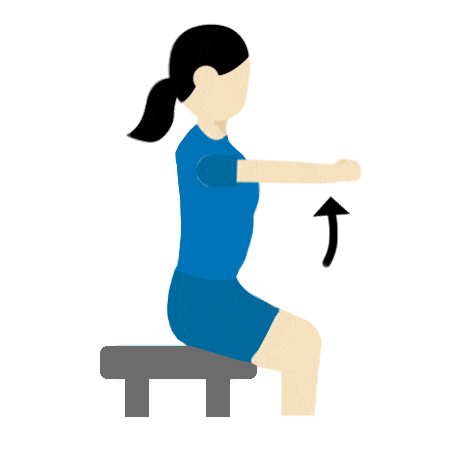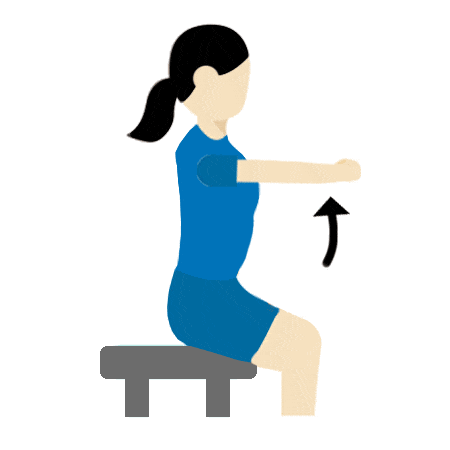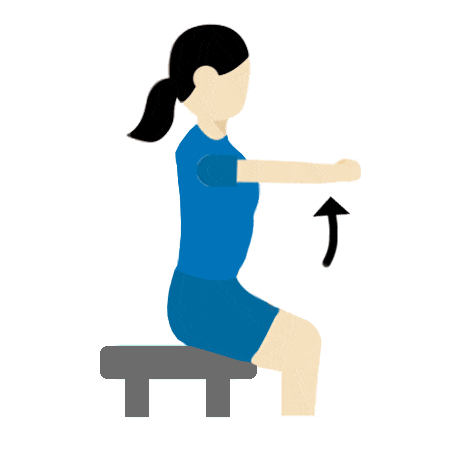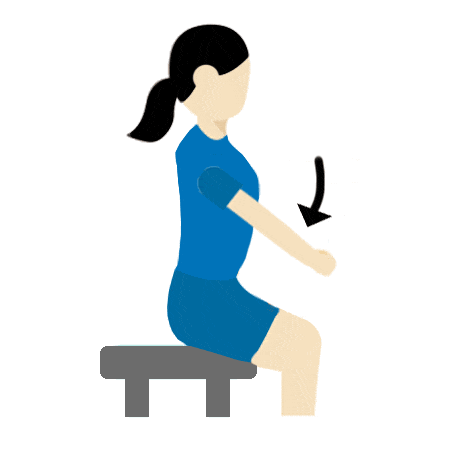
Shoulder stretch
- Keep your arms straight.
- Raise to shoulder height – hold for 30 seconds.
- Lower to knees and hold for 30 seconds.
- Repeat 5 times.
Forearm stretch
- Clasp hands together.
- Turn so stretching arm is palm-side up.
- Stretch out and hold for 30 seconds.
- Repeat for the other arm
- Repeat 5 times.
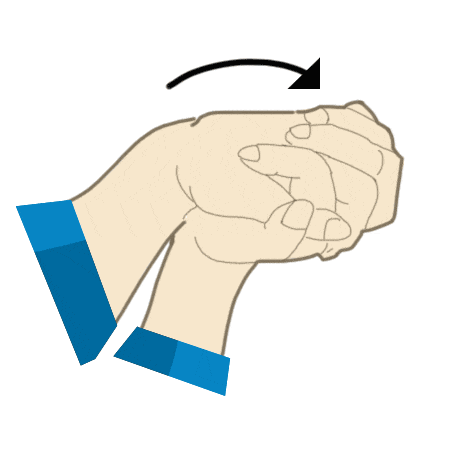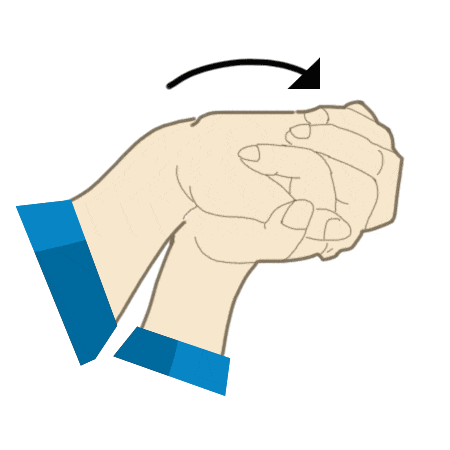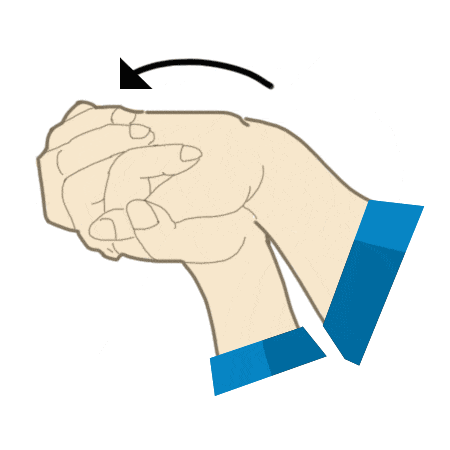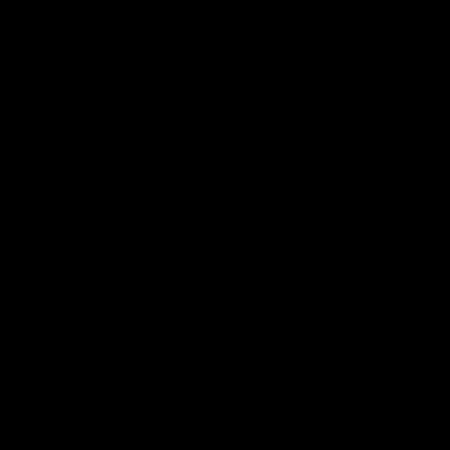
Bottle reach
- Place a bottle at end of reach.
- Clasp hands together and stretch out across table surface keeping elbows straight.
- Slide gently towards the bottle and move across until fully stretched and hold.
- Slowly bring arms back to your body bending elbows as you go.
- Repeat 7-10 times.

These basic exercises may cause a little discomfort but it shows that the muscles are strengthening. The increased tension will reduce risks of stiffening or muscle spasticity.

Intermediate exercises are great for practicing basic daily tasks. The aim of these is to kick-start neuroplasticity in the brain and reattach synaptic signals to muscle movements.
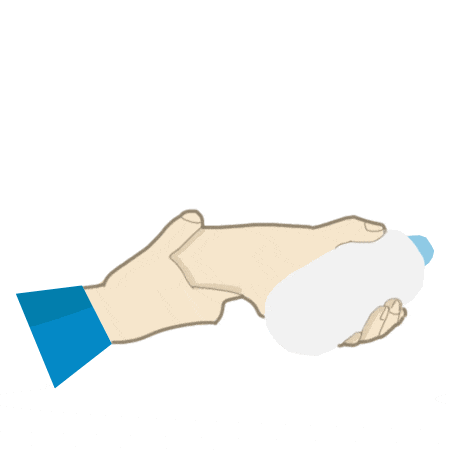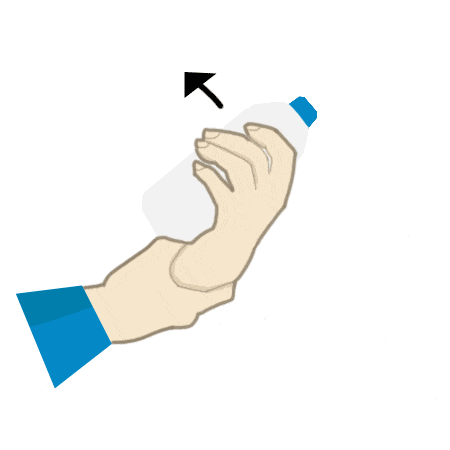
Cup Lift
- Place hand on table with elbow straight.
- Slowly wrap fingers around cup keeping thumb level with forearm.
- Lift cup up with hand with forearm staying on table before lowering back down.
- Repeat 3 times.
Bicep Lift
- Place arm on table and raise elbow to 90˚.
- Slowly move lower arm towards you as far as possible. Hold for 10 seconds.
- Slowly lower to table with arm flat on surface.
- Repeat 5 times.

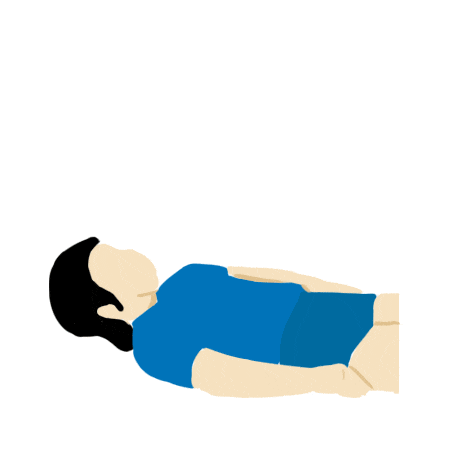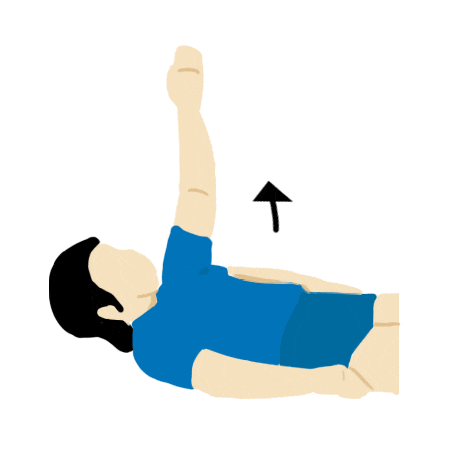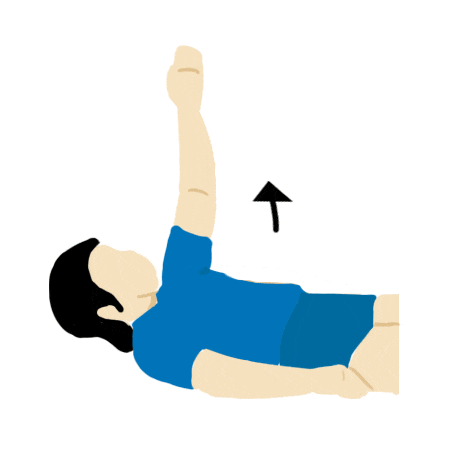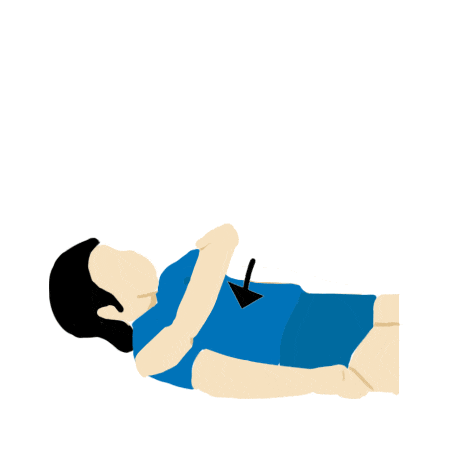
Arm and Shoulder Rotation
- Lay prone on back and slowly lift arm until straight.
- Slowly bend elbow and lower arm to touch opposing shoulder.
- Lift arm and lower down to side.
- Repeat steps for the other arm
- Repeat 3 times.
By simulating regular movements, the brain slowly rebuilds connections and allow you to perform basic tasks. Coordinating different areas of a limb gradually allows more control over your entire limb.
References:
1. Flint Rehab. (2022)
2. National University Hospital Singapore. (2022)
3. Stroke Organization New Zealand. (2017)
3. Web MD. (2012)
Website: Moleac.com
Contact: [email protected]
This document does not constitute the practice of medical consultation nor medical advice. Always seek the advice of your treating physician and/or specialist.
All Rights Reserved by Moleac Pte Ltd, Helios #09-08, 11 Biopolis Way, Singapore 138667







