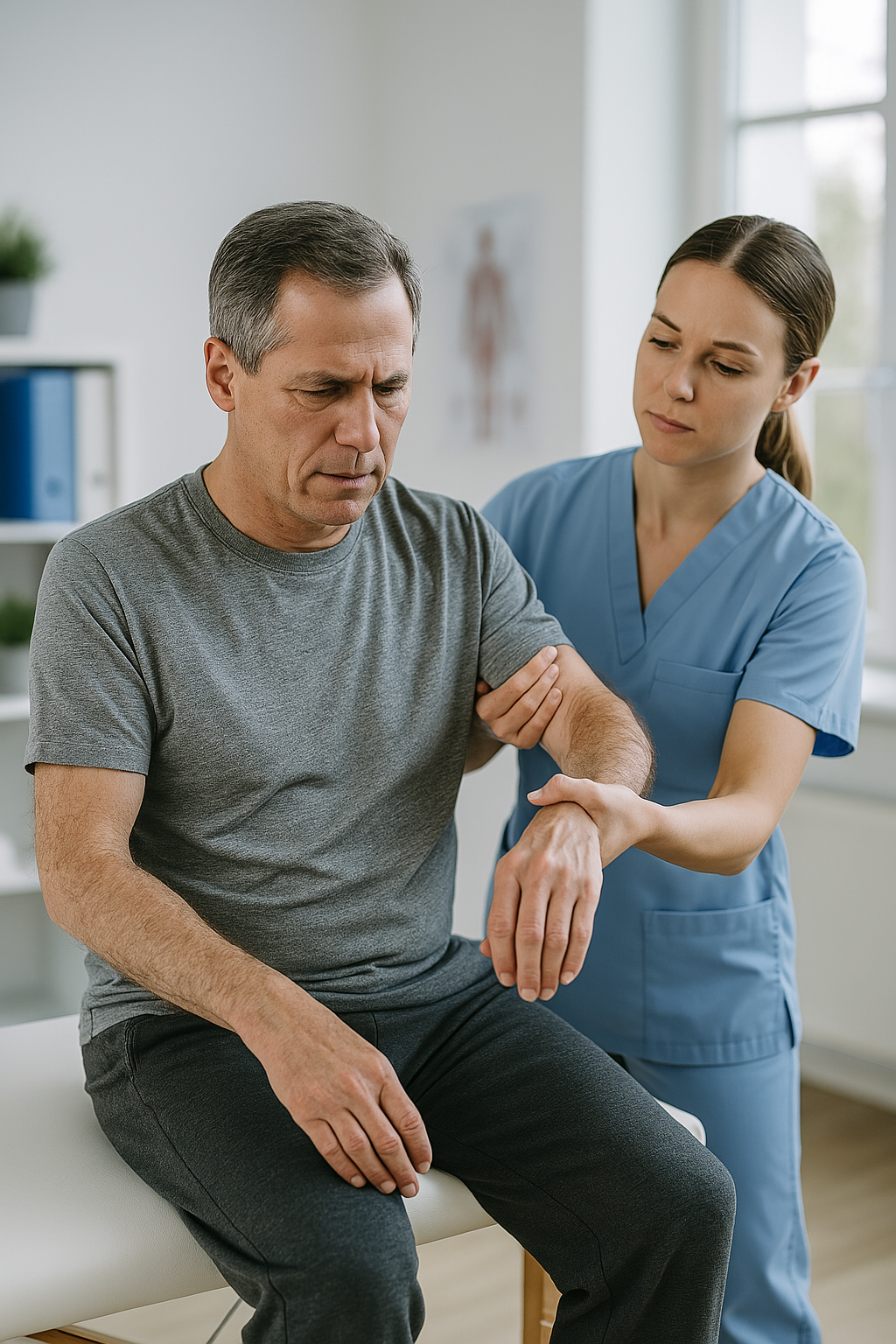
Brachiocrural hemiparesis is a neurological condition characterized by partial weakness on one side of the body, affecting both the arm and the leg on the same side. This condition is often the result of a stroke, traumatic brain injury, or degenerative neurological diseases. Recovery from brachiocrural hemiparesis depends on several factors, including the severity of the injury, early treatment, and consistency in rehabilitation.
Causes of brachiocrural hemiparesis

The main causes of brachiocrural hemiparesis include:
- Stroke: The leading cause of this condition, it occurs when blood flow to the brain is interrupted, damaging the areas responsible for movement.
- Traumatic brain injury: A strong blow to the head can cause brain damage that affects motor control.
- Brain tumors: They can exert pressure on the brain areas that control movement.
- Multiple sclerosis and other neurological disorders: These conditions can affect the transmission of motor signals.
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Conditions such as Parkinson’s disease can contribute to progressive motor weakness.
Symptoms of brachiocrural hemiparesis
Los síntomas varían dependiendo de la severidad de la lesión, pero los más comunes incluyen:
- Weakness on one side of the body: Difficulty moving the arm and leg on the same side.
- Loss of coordination and balance: This can increase the risk of falls.
- Muscle spasticity: Stiffness in the affected muscles.
- Difficulty performing daily tasks: Activities such as walking, holding objects, or getting dressed can become challenging.
- Muscle pain or discomfort: Due to prolonged lack of mobility.
- Chronic fatigue: Persistent feeling of tiredness due to the extra effort required to move.
- Sensory disturbances: Tingling or numbness in the affected limbs.
Diagnosis of brachiocrural hemiparesis
The diagnosis of brachiocrural hemiparesis is made through a combination of medical tests:
- Clinical evaluation: The neurologist performs a physical examination to assess the patient’s strength, reflexes, and coordination.
- Imaging tests: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or computed tomography (CT) help identify the cause of the hemiparesis.
- Electromyography (EMG): Evaluates the function of muscles and nerves.
- Laboratory tests: These may be conducted to rule out infections or autoimmune diseases.
- Functional mobility tests: Gait and the patient’s ability to perform daily activities are assessed.
Treatment and rehabilitation of brachiocrural hemiparesis
Treatment depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the condition. Recovery strategies include:
1. Physical therapy
Physical therapy is essential in the recovery from brachiocrural hemiparesis. It focuses on improving strength, coordination, and mobility through:
- Strengthening exercises: Targeted movements to regain strength in the affected limbs.
- Balance exercises: Improve stability and reduce the risk of falls.
- Mirror therapy: Stimulates the brain by observing movements on the healthy side.
- Therapy with assistive devices: Use of orthoses or exoskeletons to improve mobility.
- Passive and active exercises: Movement assisted by therapists or mechanical devices.
2. Occupational therapy
This therapy helps patients regain independence in daily activities such as:
- Dressing and personal hygiene.
- Writing and holding objects.
- Cooking and performing household tasks.
- Home adaptation training: Use of support bars, ramps, and ergonomic devices.
3. Speech and language therapy
If brachiocrural hemiparesis is associated with communication problems, speech therapy may be necessary to improve the ability to speak and swallow.
4. Medication
In some cases, doctors may prescribe medications to relieve symptoms:
- Muscle relaxants: To reduce spasticity.
- Anticoagulant medications: If the hemiparesis is caused by an ischemic stroke.
- Pain relievers: To ease muscle pain.
- Neuromodulators: To improve nerve function and reduce neuropathic pain.
5. Functional Electrical Stimulation (FES)
This therapy uses electrical impulses to stimulate the affected muscles and improve mobility.
6. Surgery
In severe cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to correct muscle or joint problems.
Factors influencing recovery from brachiocrural hemiparesis
Several factors can affect recovery:
- Patient’s age.
- Severity of the brain injury.
- Early initiation of rehabilitation.
- Commitment to therapy and exercises.
- Family and social support.
- Overall health status and presence of other conditions.
Tips for patients and caregivers

- Follow medical instructions precisely.
- Be consistent with rehabilitation exercises.
- Maintain a positive attitude and seek psychological support.
- Make home modifications to improve accessibility.
- Avoid risk factors such as tobacco and alcohol.
- Join support groups to share experiences and motivation.
Conclusion
Recovery from brachiocrural hemiparesis is a process that requires patience, consistency, and professional support. With appropriate treatment and a multidisciplinary approach, many patients are able to regain much of their mobility and improve their quality of life. The key lies in early rehabilitation and commitment to the recovery process. With access to innovative technologies and the support of specialists, the chances of improvement increase significantly.
If you would like more information about NeuroAiD II, please fill out this contact form.
"*" indicates required fields