NeuroAiD plays a role in the hallmarks of
Alzheimer’s Disease mechanisms
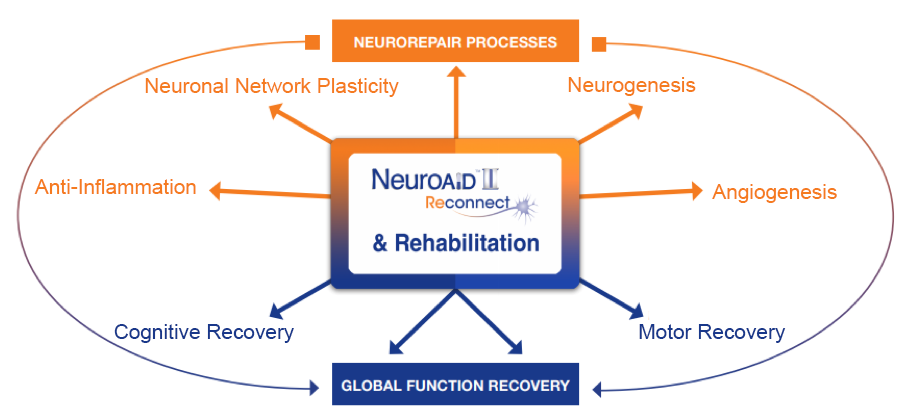
Alzheimer’s Disease (AD) results from a neurodegenerative process linked to various causes and involving several pharmacological pathways. With its multimodal mechanism of action, NeuroAiD provides an innovative approach to Alzheimer’s treatment.
NeuroAiD has a multimodal mode of action on the hallmarks of Alzheimer’s Disease mechanisms.
NeuroAiD modulates β-amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing1
Under pathological conditions such as AD, the amyloidogenic pathway of amyloid precursor protein (APP) processing results in large amount of the non-soluble and neurotoxic Aβ fragments, inducing the formation of neurofibrillary tangles. A therapeutic approach would target the APP processing to limit the amyloidogenic pathway.
An in-vitro study conducted on cultures of human neuroblastoma cells showed the effect of NeuroAiD on the APP processing 1.
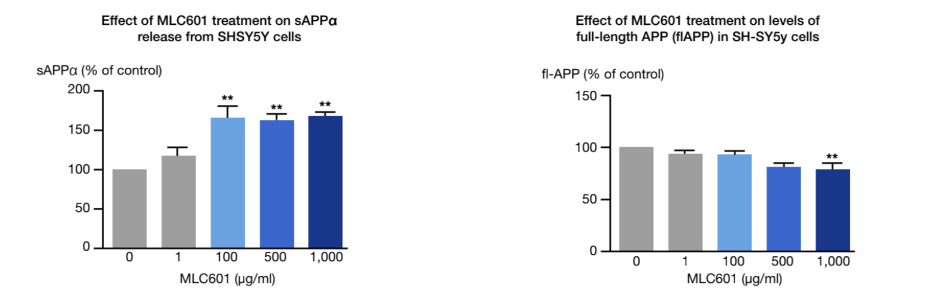
- Significantly increases the release of neuroprotective soluble fragment of APP (sAPP-α).
- Significantly decreases the levels of neurotoxic full-length APP (fl-APP).
NeuroAiD has an anti-tau phosphorylation effect2
The hyperphosphorylation of the tau proteins is another neuropathological hallmark of AD. An in-vivo study showed that NeuroAiD is impacting this process 2.

- Significantly decreases tau phosphorylation formation.
- Inhibits glycogen synthase 3β (GSK-3β) and cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (cdk5) involved in the hyper-phosphorylation process.
AT8: monoclonal antibody used in western blotting to measure tau phosphorylation
PHF: paired helical filament used in western blotting to measure tau phosphorylation
Effective and well tolerated treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease
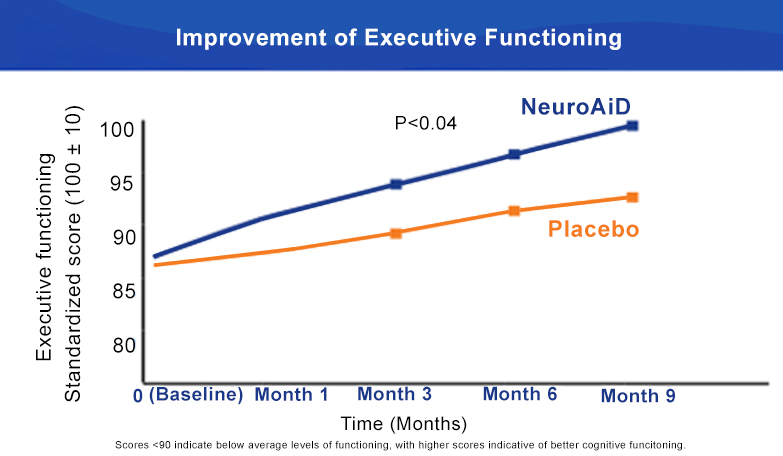
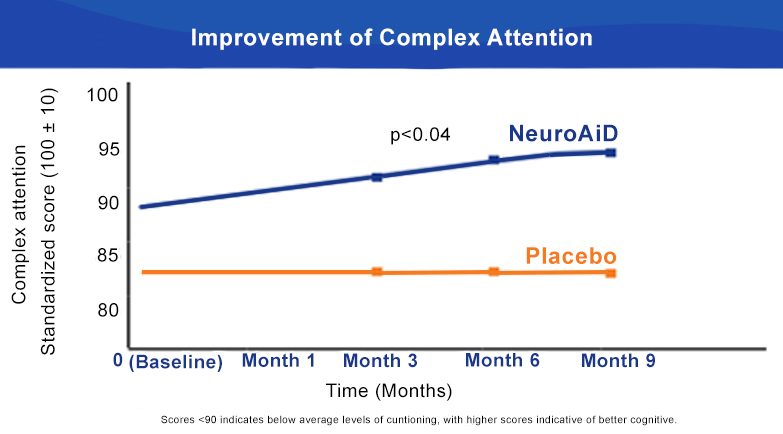
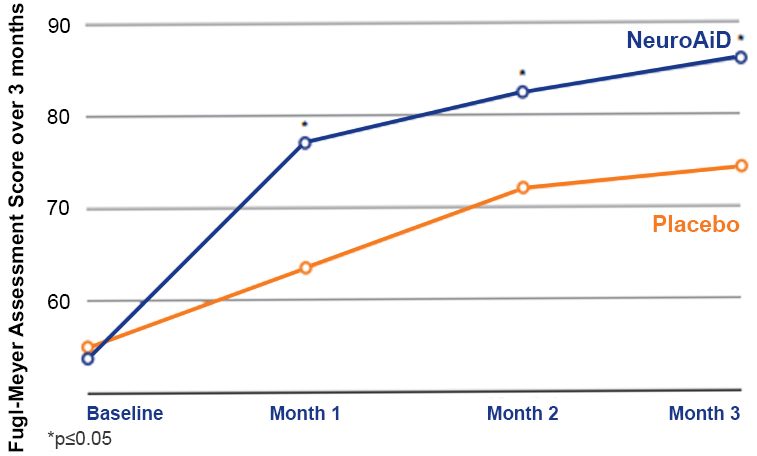
NeuroAiD improves cognitive outcomes and slows down disease progression3
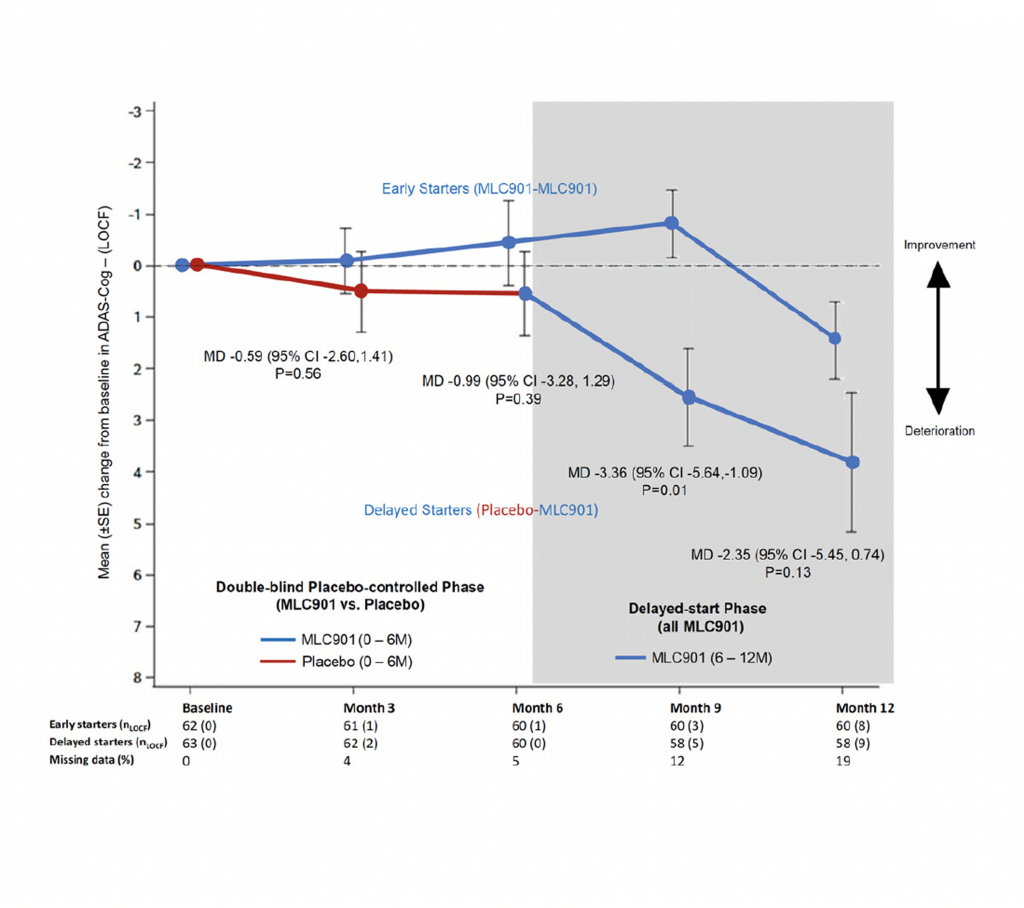
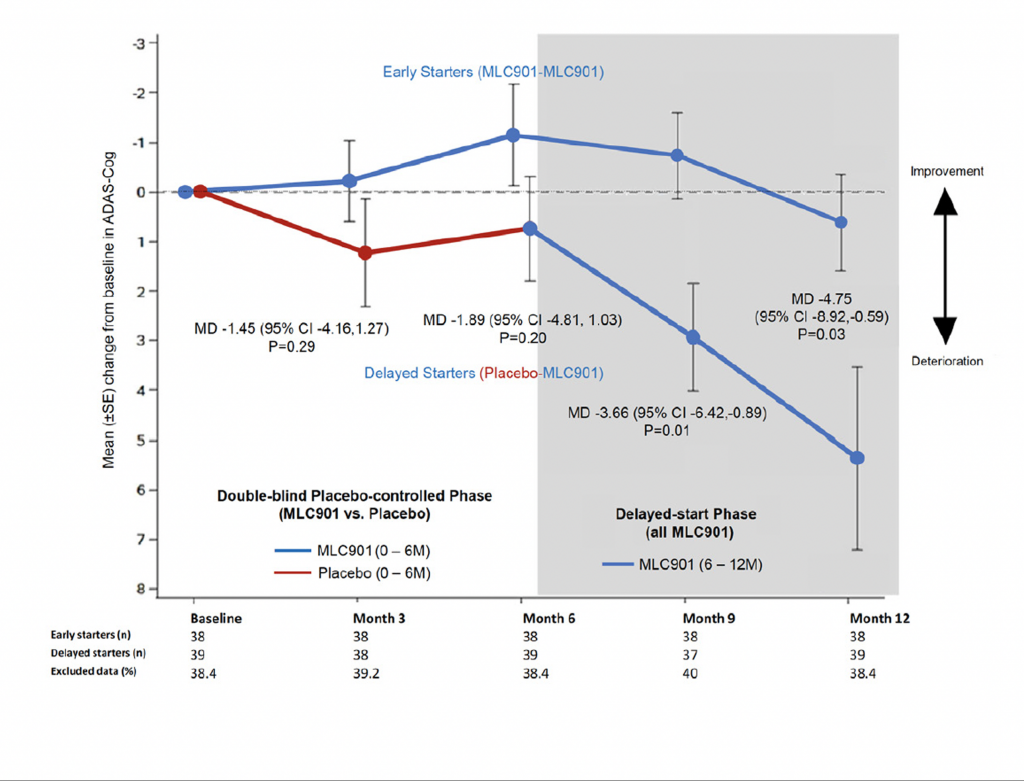
The ATHENE study 3
A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial conducted on 125 mild-to-moderate probable AD subjects, receiving NeuroAiD (MLC901, 2 capsules, 3 times a day) or placebo as an add-on therapy to standard AD treatment for 6 months, followed by an open-labelled extension study where all subjects received NeuroAiD in addition to standard of care.
- Early initiation of NeuroAiD combined with standard of care improves the cognitive function of mild-to-moderate AD patients.
- Improvements on ADAS-Cog are observed as early as month 3 and peaked at month 9.
- Favourable safety profile and tolerability in combination to standard treatment for Alzheimer.
Comparison of mean change in Alzheimer’s Disease Assessment Scale-Cognivtive subscale (ADAS-Cog) score between early starters and delayed starters
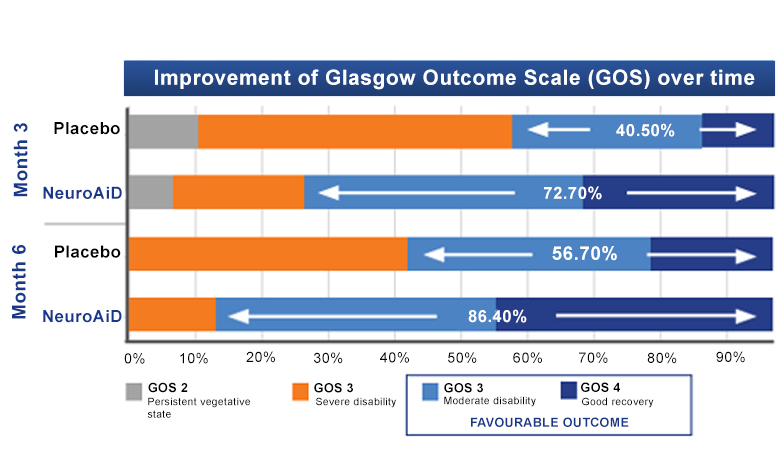
NeuroAiD is value-added over the long term with a favourable safety profile4,5,6
Open-label pilot study including 124 Alzheimer’s disease patients who failed to benefit from a previous 6-month course of Rivastigmine (lack of efficacy and/or poor tolerability), receiving NeuroAiD for 4 years. Cognitive state of the subjects was assessed by MMSE and ADAS-Cog every 6 months.4*,5*
- Significant improvement in cognitive function over the first 6 months.
- Long-term efficacy with a substantial slowdown of disease progression over 4 years observed on ADAS-Cog and MMSE.
- Good tolerability in AD patients reported up to 4 years.
In a multicentre, randomized, controlled trial conducted on 264 patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s Disease, NeuroAiD was compared to 3 approved cholinesterase inhibitors (i.e. Donepezil, Rivastigmine, Galantamine) for 16 months.6*
- NeuroAiD showed a promising effect with a similar efficacy as the 3 cholinesterase inhibitors, and a superior tolerability without adverse event-related dropouts versus 2% to 5% in acetyl-cholinesterase inhibitors’ arms.
References
- Lim YA, Murray LA, Lai MKP and Chen C (2013) NeuroAiD®(MLC601) and Amyloid Precursor Protein Processing. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2013;35(s1):30–37. Doi:10.1159/000346236
- Lee WT, Hsian CCL and Lim YA. The effects of MLC901 on tau phosphorylation. NeuroReport. 2017;28(16):1043–1048. Doi:10.1097/WNR.0000000000000884.
- Chen C, et al. Alzheimer’s Disease THErapy With NEuroaid (ATHENE): A Randomized Double-Blind Delayed-Start Trial. J Am Med Dir Assoc. 2022;379-386. Doi:10.1016/j.jamda.2021.10.018
- Pakdaman H, Gharagozli K, Abbasi M et al. Efficacy and Safety of MLC601 in Patients with Mild to Moderate Alzheimer Disease: An Extension 4-Year Follow-Up Study. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 2018;8(1);174–179. doi://10.1159/000488482
- Harandi A, Ashrafi F, Tabatabaei M et al. “Efficacy and Tolerability of MlC601 in Patients with Mild to Moderate Alzheimer Disease Who Were Unable to Tolerate or Failed to Benefit from Treatment with Rivastigmine.” Br J Med Med Res. 2013;3:341-350. Doi: 10.1159/000488482
- Pakdaman H, Harandi AA, Hamidreza H et al. Effectiveness and safety of MLC601 in the treatment of mild to moderate Alzheimer’s Disease: a multicenter, randomised controlled trial. Dement Geriatr Cogn Dis Extra. 2015;5(1):96-106. Doi:10.1159/000375295
* Studies conducted with NeuroAiD MLC601 at 1 capsule, 3 times a day.
NeuroAiDTM is a trademark of Moleac. MLC601 (NeuroAiDTM) and MLC901 (NeuroAiDTMII/ NurAiDTMII) are two different proprietary formulae which have been shown to be equivalent in pharmacology and are referred as “NeuroAiD” in this document.


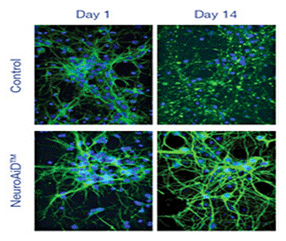 Effects of MLC601/MLC901 treatment on in vitro Synaptotagmin 1 expression in cultured cortical neurons. Synaptotagmin 1 expression was analyzed after MLC601/MLC901 treatment (1 mg/ml) at Day 7 and 14 of treatment.
Effects of MLC601/MLC901 treatment on in vitro Synaptotagmin 1 expression in cultured cortical neurons. Synaptotagmin 1 expression was analyzed after MLC601/MLC901 treatment (1 mg/ml) at Day 7 and 14 of treatment.
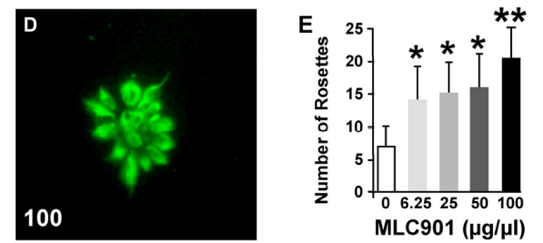 Neurogenic effects of MLC901 on human ESC-derived progenitors. (D) Radiant rosette-like aggregates of nestin-positive neural progenitors spontaneously form in low-density cultures. (E) Quantification of the number of rosettes 2 days after the addition of MLC901 (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus control).
Neurogenic effects of MLC901 on human ESC-derived progenitors. (D) Radiant rosette-like aggregates of nestin-positive neural progenitors spontaneously form in low-density cultures. (E) Quantification of the number of rosettes 2 days after the addition of MLC901 (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 versus control).