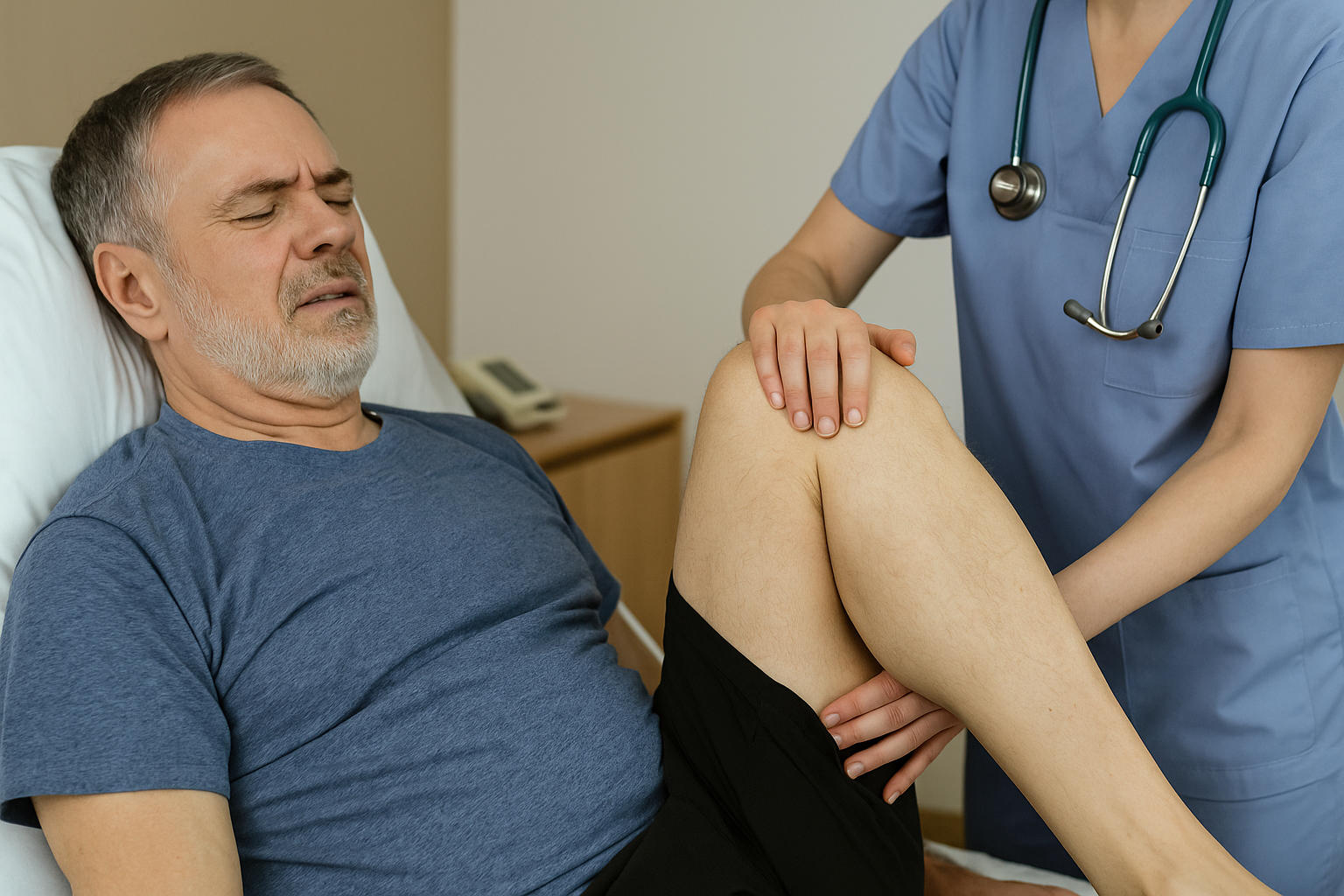
After a stroke, the body may experience a range of physical aftereffects, among which muscle spasms are quite common. These involuntary contractions affect mobility, causing discomfort and even pain. It’s natural to want to know how to relieve a muscle spasm and regain better control of movement.
What is a muscle spasm?
A muscle spasm is a sudden, involuntary contraction of one or more muscles. It can last from a few seconds to several minutes. In individuals who have suffered a stroke, these spasms are often caused by damage to the nervous system that disrupts communication between the brain and the muscles.
Before learning how to relieve a muscle spasm, it is important to understand that after a stroke, the risk of stiffness and spasticity increases significantly, affecting quality of life.
Why do muscle spasms occur after a stroke?

After a stroke, certain areas of the brain responsible for controlling movement become damaged. This leads to muscle incoordination, weakness, and in many cases, spasms. Understanding how to relieve a muscle spasm involves recognizing that in these patients, the issue is not only muscular but also neurological.
Factors that increase the occurrence of spasms after a stroke:
-
Severe damage to motor areas of the brain.
-
Limited mobility during the early stages of recovery.
-
Muscle contractures or poor positioning while lying down or sitting.
How to safely relieve a muscle spasm after a stroke?
The strategy for managing post-stroke spasms combines several methods:
-
Apply heat: Heating pads help relax the contracted muscle.
-
Perform gentle stretches: Controlled movements, always guided by a physical therapist.
-
Therapeutic massages: Improve circulation and reduce stiffness.
-
Passive mobilization: In the early stages, the physical therapist moves the limbs to prevent stiffness.
-
Proper hydration: Lack of fluids can worsen spasms.
Using these techniques is part of the practical approach to relieving a muscle spasm in patients who have suffered a stroke.
Specific medical treatments
When home methods are not enough, there are medical treatments that can help in understanding how to relieve a muscle spasm in this context:
-
Muscle relaxant medications: Such as baclofen or tizanidine.
-
Botulinum toxin: Injections that relax specific affected muscles.
-
Electrical stimulation therapies: Help activate weak muscles and reduce spasms.
In all cases, treatment should be personalized and always supervised by professionals specialized in neurological rehabilitation.
¿Qué ejercicios ayudan a quitar un espasmo muscular tras un ACV?
El movimiento es clave. Algunos ejercicios recomendados son:
-
Estiramiento de extremidades: Suaves y progresivos, para evitar lesiones.
-
Rotaciones articulares: De hombros, caderas, muñecas y tobillos.
-
Técnicas de fortalecimiento muscular: Para recuperar el control motor.
La constancia en estos ejercicios es vital para entender cómo quitar un espasmo muscular de manera progresiva y segura tras un accidente cerebrovascular.
Importancia de la fisioterapia temprana

La rehabilitación inmediata después de un ACV puede reducir considerablemente el riesgo de espasmos. Iniciar fisioterapia dentro de los primeros días mejora el pronóstico y facilita cómo quitar un espasmo muscular en las fases posteriores de recuperación.
Además, los fisioterapeutas enseñan técnicas de manejo de espasticidad, uso de ortesis y ejercicios que favorecen la movilidad, esenciales en el proceso de recuperación.
Consejos para prevenir futuros espasmos musculares
Una vez que se ha aprendido cómo quitar un espasmo muscular, es fundamental también prevenir su aparición:
-
Mantener una rutina de ejercicios diarios.
-
Hidratarse adecuadamente.
-
Evitar posiciones prolongadas en cama o silla.
-
Usar dispositivos de apoyo (férulas, cojines especiales) recomendados por el terapeuta.
Estos hábitos diarios tienen un impacto enorme en la calidad de vida de los sobrevivientes de un ACV.
Reflexión final
Sufrir un accidente cerebrovascular implica enfrentarse a nuevos desafíos físicos y emocionales. Entre ellos, los espasmos musculares pueden ser especialmente frustrantes. Sin embargo, entender cómo quitar un espasmo muscular permite a los pacientes y sus familias actuar de forma informada y positiva.
Con tratamientos adecuados, fisioterapia temprana, ejercicio regular y apoyo médico, muchos sobrevivientes de un ACV logran recuperar movilidad, autonomía y calidad de vida. El primer paso siempre será informarse, buscar ayuda profesional y mantener una actitud perseverante.
If you would like more information about NeuroAiD II, please fill out this contact form.
"*" indicates required fields