Treatment of muscle spasticity is a disorder characterized by stiffness and excessive muscle contraction, which can limit mobility and affect the quality of life of those who suffer from it. Fortunately, there are various treatment options for muscle spasticity that can help reduce symptoms and improve patients’ functionality.
Physical Therapy
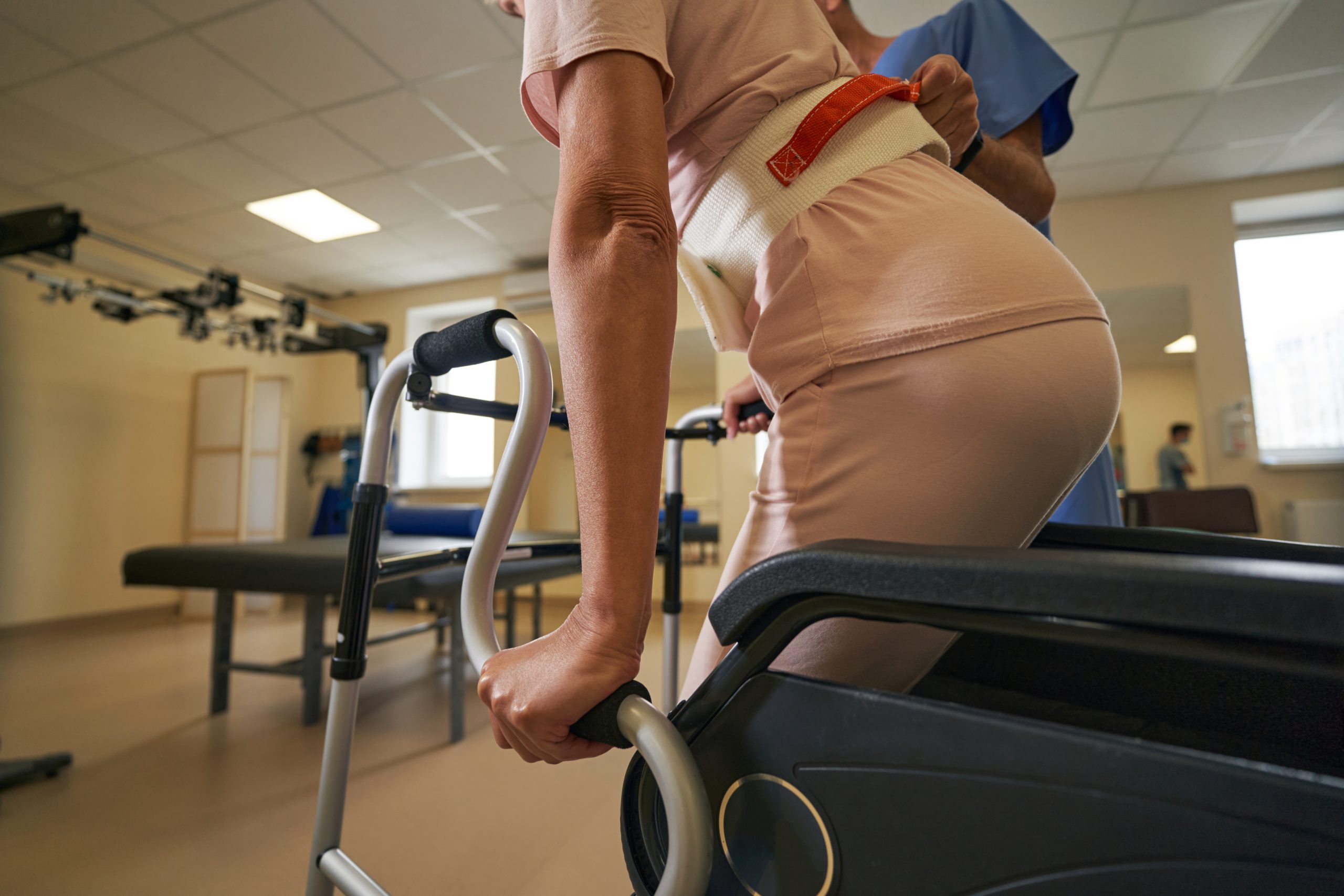
Physical therapy plays a fundamental role in the management of muscle spasticity. Physical therapists use a variety of techniques, such as stretching, muscle strengthening exercises, and both active and passive mobilization, to improve flexibility and motor function. These therapeutic approaches help reduce muscle stiffness and improve range of motion.
Muscle Stretching
Muscle stretching is essential for improving flexibility and reducing muscle stiffness. Physical therapists can teach specific stretching exercises that target the muscle groups affected by spasticity. These stretches are performed regularly and correctly to maintain muscle length and elasticity.
Strengthening Exercises
Muscle strengthening is essential for improving function and muscle control. Physical therapists may recommend strengthening exercises that target weak and imbalanced muscles.  These exercises may include light weightlifting, elastic resistance, or bodyweight exercises, all adapted to the individual needs of each patient.
These exercises may include light weightlifting, elastic resistance, or bodyweight exercises, all adapted to the individual needs of each patient.
Gait Training
Gait training focuses on improving the walking ability of patients with muscle spasticity. It may include techniques such as weight-supported walking, assistive devices (like crutches or walkers), or even the use of advanced technologies such as functional electrical stimulation (FES), which helps activate weakened muscles during walking.
Aquatic Therapy
Aquatic therapy, performed in a pool or controlled aquatic environment, can be beneficial for people with muscle spasticity. Water provides buoyancy, which reduces joint load and facilitates movement. Additionally, the resistance of the water can help strengthen muscles without placing excessive stress on them.
Relaxation Techniques
Stress and emotional tension can worsen muscle spasticity. Therefore, relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga can be helpful in reducing muscle stiffness and promoting overall relaxation. These techniques can be combined with physical therapies to enhance overall outcomes.
It is important to emphasize that each patient is unique and responds differently to physical therapies. Therefore, it is essential to work closely with a physical therapist specialized in muscle spasticity to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
Medications
There are several medications used to treat muscle spasticity. Muscle relaxants, such as baclofen and tizanidine, are commonly prescribed to reduce stiffness and improve muscle function. Additionally, certain medications, such as botulinum toxin type A, can be injected directly into the affected muscles to temporarily block the release of chemicals responsible for excessive muscle contraction.
Occupational Therapy
Occupational therapy focuses on improving functional skills and independence in daily living activities for patients with muscle spasticity. Occupational therapists can teach techniques and adaptations to make everyday tasks easier, as well as recommend assistive devices, such as orthotic appliances or wheelchairs, to enhance mobility and quality of life.

Surgery
In certain cases, when non-invasive treatments fail to relieve the symptoms of muscle spasticity, surgery may be considered. Surgical procedures such as selective dorsal rhizotomy or selective neurectomy involve interrupting the nerve pathways responsible for excessive muscle contraction, which can result in a significant reduction of spasticity.
Conclusion on the Treatment of Muscle Spasticity
In conclusion, the treatment of muscle spasticity is a broad and diverse topic, but there are effective options and approaches that can help improve the quality of life for those who suffer from it. The combination of physical therapy, medications, occupational therapy, baclofen pump therapy, and, in selected cases, surgery provides a range of therapeutic options to address muscle spasticity from different angles.
Physical therapy plays a fundamental role in improving mobility, flexibility, and motor function through techniques such as stretching, muscle strengthening exercises, and gait training. Medications, such as muscle relaxants and botulinum toxin, can be used to reduce muscle stiffness and improve function. Occupational therapy focuses on improving functional skills and independence in activities of daily living. In more complex cases, baclofen pump therapy or surgery may be considered for more precise control of spasticity.
It is important to emphasize that the treatment of muscle spasticity must be personalized and tailored to the individual needs of each patient. A multidisciplinary approach involving doctors, physical therapists, occupational therapists, and other health professionals is essential to achieve the best results.
In summary, the treatment of muscle spasticity is based on a comprehensive approach that combines different therapies and strategies. With proper care and collaboration between the patient and the medical team, it is possible to reduce the symptoms of muscle spasticity, improve function, and promote a better quality of life.
If you need information about NeuroAiD II, you can fill out this contact form.
"*" indicates required fields